Ting-Chi Lo, Wen-Jyun Wang, Chih-Yen Chen*, Jui-Cheng Chang*, and Wei-Peng Li*
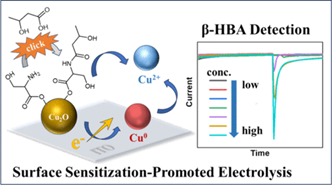
With the global prevalence of diabetes continuously increasing, there is a rapidly expanding market for home health monitoring devices. Although blood glucose monitoring technologies are well-established, current methods for detecting diabetic ketoacidosis remain inadequate. Addressing this gap, Prof. Wei-Peng Li’s team, in collaboration with Prof. Chih-Yen Chen from the National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University and Prof. Jui-Cheng Chang from the Chung Yuan Christian University, developed an innovative electrochemical detection method utilizing serine-modified Cu2O nanoparticles as electrode materials. By engineering serine groups on the surface of Cu2O nanoparticles, the research team facilitated a click-like esterification reaction between the nanoparticles and β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HBA), resulting in stable deposition of β-HBA onto the electrode surface. Quantitative analysis of β-HBA was then performed using amperometric measurements, which revealed a high linear correlation between the reduction current and β-HBA concentration over a range of 0–20 mM, achieving a detection limit of 0.1 mM. Moreover, cyclic voltammetry experiments demonstrated an electrolysis enhancement mechanism attributed to small-molecule analytes effectively covering nanoparticle surfaces. This groundbreaking small-molecule detection mechanism paves the way for designing future portable electrochemical sensors. This research has been accepted by the prominent physical chemistry journal Langmuir (2025, 19, 12022) and was selected as the supplementary cover.
Reference:
Ting-Chi Lo, Wen-Jyun Wang, Chih-Yen Chen*, Jui-Cheng Chang*, and Wei-Peng Li*. Serine-Grafted Cu2O Electrode Enabling Specific β-Hydroxybutyrate Detection by Surface Sensitization-Promoted Electrolysis in Amperometry. Langmuir, 2025, 19, 12022-12029. (selected as the supplementary cover)
